At Branching Minds, we believe that in order for Multi-Tiered System of Supports (MTSS) to be effective and objective, it must address the whole child. This includes understanding and supporting students’ social-emotional learning and development. With the mounting evidence highlighting the importance of SEL within schools, it is exciting to see so many districts embrace SEL and work towards making it an integral part of their educational goals.
However, there has recently been some pushback against SEL from some administrators, teachers, parents, and community members. This has largely come from misinformation being spread about what SEL is. SEL is not a political movement or part of a political agenda. It is focused on helping children and adolescents develop skills that are critical for their long-term success. It is not meant as a tool to make students focus and control or suppress their emotions and behaviors; it is about making them more aware of their emotions and their connections to behaviors. It is about helping students be aware of the thoughts, feelings, and perspectives of others to help them build positive relationships and be able to collaborate with others, and have a strong sense of connection and belonging within their classrooms and schools. If we want our students to have successful long-term outcomes, beyond just their grades and test scores, teaching these skills needs to be integrated into education.
SEL is not a one size fits all approach. What works for one district, school, or community might not translate to another. That’s why school and district leaders need to collaborate with families, students, and other key stakeholders to develop SEL goals and initiatives. And when it comes to selecting SEL assessment and programs, there should be attention towards what exactly they are measuring and teaching, as well as the evidence supporting their effectiveness.
We hope that this guide can help your district better understand SEL and make these critical decisions about assessment, programs, interventions, and how to best think about and integrate these components into existing MTSS frameworks.
Three key takeaways from this CASEL’s definition:
- SEL is a Mechanism for Addressing Educational Inquiry
- Identity, Agency, and Belonging are Critical Social-Emotional Assets
- SEL Should Be Integrated Into the Broader Curriculum and Learning Contexts
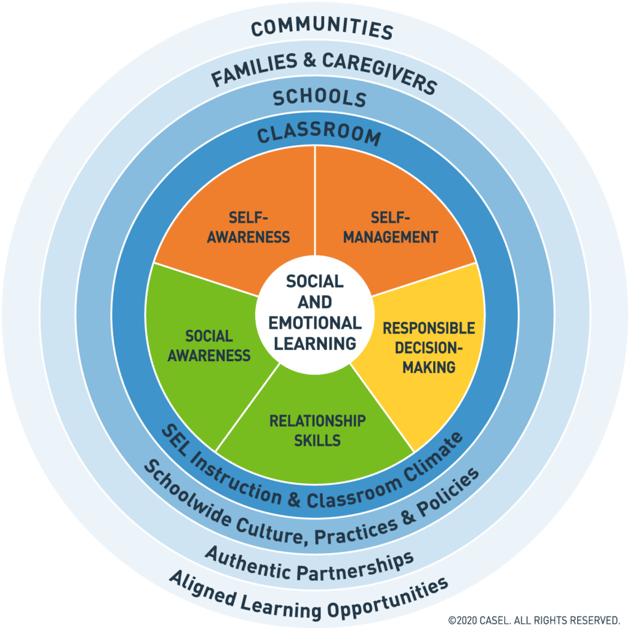
CASEL’s Five Core Competencies
CASEL stands for the Collaborative for Academic and Social-Emotional Learning. Described as “a trusted source for knowledge about high-quality, evidence-based social and emotional learning (SEL)”, CASEL is a leading entity on SEL research. CASEL provides SEL-based resources for educators, researchers, and policy-makers. The organization has a number of initiatives all focused on improving student and teacher social-emotional learning and development. Some of their most popular resources include their program guide, which helps educators identify their SEL goals and priorities and find evidence-based programs aligned to those goals, as well as their assessment guide, which provides filterable lists of assessments that measure different social-emotional competencies across all grade levels and their corresponding research/evidence. These resources are why many districts turn to CASEL when looking for support in promoting SEL in their schools, classrooms, and communities.
What are the Five Core Competencies?
CASEL provides five core competencies for defining and describing what SEL is and how to implement it effectively.
- Self-Awareness - Personal and sociocultural identities, recognition of beliefs, mindsets & biases
- Self-Management - Stress management, self-care, perseverance, agency
- Social Awareness - Perspective-taking, empathy, belonging
- Relationship Skills - Collaborative problem solving, co-construction, effective interpersonal communication
- Responsible Decision-Making – ethical responsibility, distributive justice, collective well-being
.gif)
Learn How to Support the Whole Child with Branching Minds
Branching Minds makes MTSS easy, efficient, and effective by bringing together all of the components of MTSS so teachers can collaboratively problem-solve and support all students’ holistic needs. Our system-level solution helps schools improve students’ outcomes across academics, behavior, and SEL equitably. Click here to learn more.
SEL Within MTSS
-
What is MTSS
Multi-Tiered System of Support (MTSS) is a collaborative, evidence-based, approach to differentiating and personalizing instruction and intervention, across academics, social-emotional learning and behavior for all students—so that every student can achieve academic and life success.
MTSS is one of the most effective ways to provide an equitable educational experience because it leverages collective knowledge and expertise to help teachers understand their learners' needs and make informed and strategic decisions that best support them.
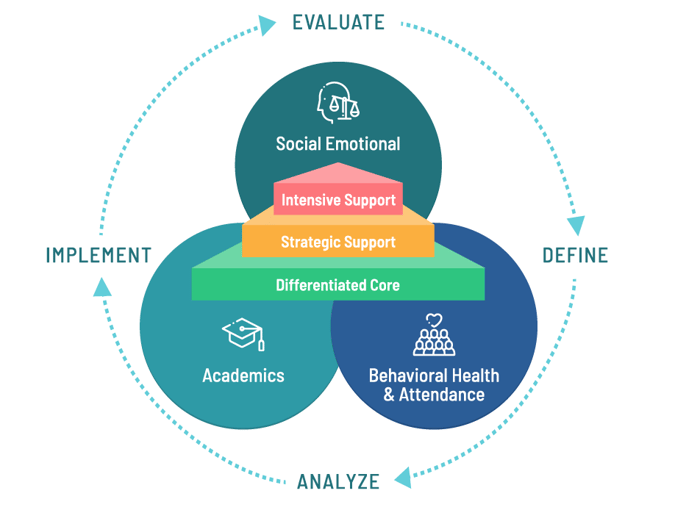
MTSS begins with teachers assessing the skills of everyone in the class, to proactively identify who may need additional support in an area (e.g. reading, math, behavior). Students then receive support (research-based, targeted instruction or intervention) matched both to their skills and level of need. Those students’ progress is monitored closely to ensure that the additional support is helping. If the achievement gap has resolved, the additional support in that area is no longer required; if it does not improve, then the level of personalization increases, further problem solving to understand why each student struggles, and to design a customized plan to support their needs in a defined and systematic way.
-
The essential components of MTSS
- Screening
- Multi-Level Prevention System
- Progress Monitoring Assessments
- Data-Based Decision Making
Read more about the Essential components of MTSS
Integrating SEL into an MTSS Framework
In MTSS, SEL is integrated as a system-level approach, where collective leadership includes all stakeholders into the decision-making process. SEL intervention is driven by data retrieved from SEL assessments and progress monitors, and SEL components can be embedded into academic content. Additional non-academic SEL supports (such as counseling) can provide additional intervention for identified students.
-
Core Components of SEL in MTSS:
- Universal Screening for SEL
🔘 Evidence-based assessments, such as The DESSA (Aperture Education), are used to identify students needing SEL support and intervention. SEL screeners are reliable, valid, sensitive, and specific. - Programs and Supports
🔘 SEL programs are sequenced, active, focused, and explicit to targeted skills. They are evidence-based and implemented with fidelity. SEL programs should be easily integrated into core curriculums with transferable skills, and aligned to student needs. An example of a SEL program is Harmony SEL. - Progress Monitoring Assessments
🔘 Progress monitoring assessments are used to measure progress of students requiring SEL intervention support at the Tier 2 or Tier 3 level. SEL progress monitoring assessments, such as behavior trackers, can be used to document a student’s daily classroom behavior. This data can be used to determine if a student requires more intensive support or is showing improvement with the current plan.
🔘 Schools can use a SEL screener or assessment once a month to measure SEL progress and identify students who need additional support.
- Universal Screening for SEL
Benefits of SEL
Incorporating an evidenced-based curriculum into academic content has been proven to lead to:
- Improved academic performance for all students
- Improved social skills and sense of belonging
- Reduction of behavior interruptions and negative behavior incidents
- Positive school climate
Beyond the classroom, a robust SEL program can also provide students and staff with lifelong skills. These skills include:
- Postsecondary success and completion for students
- Success in the workplace for students and staff
- Adult mental health skills and strategies, positive relationships, and increase overall well-being
SEL Assessments
Similar to the academic assessments utilized in an MTSS framework, SEL assessments can be utilized to identify students requiring additional SEL support and as a monitor for overall system-level support and health. There are two tools for SEL assessments that educators can use: universal screening assessments and progress monitoring assessments.
Universal screening assessments for SEL
The use of universal screening assessments for SEL allow school leaders and educators to:
-
Identify school- and grade-level SEL trends
-
Inform school-wide programs and practices
-
Support the need for professional development
-
Identify students who need additional support
-
Identify specific areas of needed support
Progress monitoring assessment for SEL
The use of a progress monitoring assessment for SEL allow school leaders and educators to:
-
Evaluate the impact and effectiveness of Tier 2 and Tier 3 supports and interventions
-
Use behavior trackers to document student daily progress. For example: daily classroom behavior
-
Progress monitoring assessments may use a SEL universal screener tool to frequently monitor SEL progress
When selecting an SEL assessment tool, it is important to select a normed assessment that is reliable, valid, sensitive, and specific. When selecting an assessment tool, educators should ask the following questions:
- Is this assessment measuring what it is supposed to be measuring?
- Does this assessment accurately identify students who need support?
- Will this assessment over-identify or under-identify students?
- Will this assessment provide clear and reliable data to target instruction and intervention?
Student’s Self-Assessment: SECA
The Social Emotional Competency Assessment (SECA) is a student-facing survey for students in grades 5-12. The assessment measures eight social-emotional skills:
- 1) self-awareness of strengths and weaknesses
- 2) self-awareness of emotions
- 3) self-management of emotions
- 4) self-management of goals
- 5) self-management of school work
- 6) relationship skills
- 7) social awareness
- 8) responsible decision-making
The SECA has shown evidence of reliability and validity. Items were shown to assess a broad range of student social-emotional skills and abilities. While controlling for a number of demographic and academic factors, students who scored higher on the SECA (compared to students who scored lower) had significantly higher reading and math test scores and weighted GPAs and lower suspension rates and absenteeism (Crowder, Gordon, Brown, Davidson, & Domitrovich, 2019)
Data from the SECA can be used to evaluate school or grade-level social-emotional health. This data can further inform the SEL intervention process for middle school and secondary students to ensure that student perspectives on their own social-emotional skills and sense of well-being are leveraged when developing intervention plans.
Assessing SEL Needs with the DESSA
Grounded in resilience theory and directly aligned to the CASEL framework, the DESSA is a user-friendly, practical social-emotional learning assessment that meets the highest professional standards. It is a standardized, strength-based social-emotional and behavior assessment designed to measure social-emotional competence for students in grades K-12.
The DESSA suite of assessments includes the following:
- The DESSA-mini: A valid and reliable one-minute screener of students’ social and emotional competence. The DESSA-mini provides insight for students in grades K-8.
- The DESSA: The flagship assessment of Aperture Education*. A valid and reliable 72-item assessment of social and emotional strengths and needs for students in grades K-8.
- The DESSA-High School Edition-mini (DESSA-HSE mini): A valid and reliable one-minute screener of students’ social and emotional competence for students in grades 9-12.
- The DESSA-High School Edition (DESSA-HSE): A valid and reliable 43-item assessment of social and emotional strengths and needs for students in grades 9-12.
*Aperture Education
Aperture Education has a long track record of helping teachers assess students’ social-emotional competencies, monitor progress, and measure outcomes of students in grades K-12, in a strengths-based format. Grounded in resilience theory and directly aligned to the CASEL framework, Aperture Education’s assessment, the DESSA, is a standardized user-friendly, practical social-emotional learning assessment that meets the highest professional standards. The partnership between BrM and Aperture allows districts to administer the DESSA-mini screener and DESSA diagnostic assessments directly through the BrM platform, as well as view results for individual and groups of students. Aperture and BrM have also partnered on webinars and conference focused on using SEL assessments within MTSS.
Related Resources:➡️ How to Measure SEL - 7 Approaches to Consider |
SEL Programs
An important part of integrating SEL into an MTSS framework is the utilization of evidence-based programs and practices that effectively target identified skill areas and support student SEL growth and progress. SEL interventions and supports can be used to support individual students as well as school-wide programs that facilitate and foster overall system-level SEL.
SEL interventions and supports should be research-based, implemented with fidelity, and evaluated with valid and reliable assessments.
Examples of Research-Based SEL Programs:
Harmony SEL is an evidence-based CASEL SELect program. It includes scaffolded lessons across six units addressing key social-emotional competencies as well as everyday practices to build awareness of self and others and develop meaningful connections in the classroom. Harmony SEL’s professional development platform, Harmony Inspire, can also be used by educators to further develop their own social-emotional competencies and to help implement SEL in their classrooms.
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) is an evidence-based three-tiered framework to improve and integrate all of the data, systems, and practices affecting student outcomes every day.
The Random Acts of Kindness foundation is a non-profit organization that aims to build kindness, compassion, and empathy in schools. Their evidence-based SEL program, Kindness in the Classroom, consists of lessons and activities for students in kindergarten through twelfth grade. The foundation also provides training materials for SEL implementation as well as book lists, games, and letters to engage family members in topics related to kindness in education.
How to Improve SEL
While building a strong SEL foundation is important, it is also important to continuously evaluate a SEL system for improvement and fidelity. If an SEL program already exists, consider the following steps to increase the effectiveness of social-emotional learning to support all learning.
-
Use a Competency Framework
A competency framework focuses on building the skills that promote positive behaviors. During intervention planning, instead of focusing on which behaviors to decrease, think about the competencies to improve and develop.
-
Move Beyond Behavior Tracking
Behavior monitoring tools are effective in gaining data of student behavior, yet are ineffective as an intervention. To improve the effectiveness of behavior interventions, students should be involved in the setting of their own behavior goals and determining if their goals are being met. This improves motivation and keeps students actively engaged in their own learning and self-awareness.
-
Track Implementation Fidelity
Implementation fidelity is the most important part of any SEL intervention. Some of the most well-designed, comprehensive, research-based programs fail to have any effects due to poor implementation. This can be due to many factors, such as lack of teacher training, poor student attendance, and issues with the program or curriculum itself. Implementation becomes even more important as students are learning remotely and online. District and school leaders should ensure that their teachers have adequate and appropriate training and support to implement SEL programs and practices. Teachers should also be encouraged to keep track of the quantity and quality of implementation and school leaders should be reviewing the fidelity of implementation throughout the school year.
-
Integrate SEL Lessons into Core Curriculum
SEL programs, strategies, and lessons should be incorporated and reinforced across topic areas to encourage the daily practice of SEL skills and understanding. SEL concepts should be fully integrated into academic curriculum to allow students the opportunity to practice key social-emotional skills, such as communication, problem-solving, and social awareness.
Supporting Staff Well-Being in SEL
SEL is not just for students, but also for staff members. Teaching can be one of the most stressful occupations, with high levels of stress, anxiety, and burnout. SEL programs that provide support for educators and students can help alleviate the stress and challenges which cause many educators to leave teaching.
SEL for educators can help staff members:
-
Understand and communicate their own SEL needs
-
Manage stress and anxiety
-
Foster stronger relationships with students and colleagues
-
Encourage healthy work-life balance
-
Increase mental health care and awareness
Here are some strategies to encourage SEL learning and awareness with school staff:
- Seek out SEL resources for staff
- Provide professional development around supporting SEL
- Create school-wide SEL expectations and guidelines for students and staff
- Model SEL skills for students

